

#Blind write in dbms serial
Here, we will check to get a view equivalent serial schedule:

If the specified schedule is conflict serializable after that will certainly be view serializable.We can identify whether the provided schedule is said to be conflict serializable or not by the following: Mainly, there are two kinds of serializability: 1. Here, the idea of serializability benefits for identifying the precise non-serial schedules that support the consistency of the database. The answer for this is that the system resources are completely consumed by the concurrent implementation of transactions that are significantly quicker when associated with serial schedules. It may seem to check whether a non-serial schedule is serializable instead of having a serial schedule for all time. To inspect that a definite non-serial schedule is stated to remain view serializable, we need to confirm that it holds a consistent schedule.
#Blind write in dbms how to
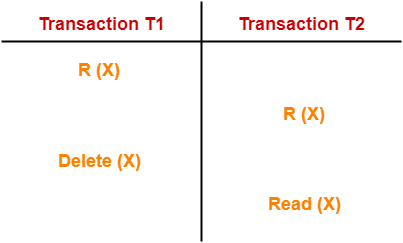
How to Perform View Serializability in DBMS? Supposing for illustration, in schedule T1, X1 implements a read procedure on Y after the writing procedure on Y by X2, then in T2, X1 must read the Y after X2 implements write on Y.
#Blind write in dbms update
Update Read: Uncertainty in schedule T1, the transaction X1 is reading any data item restructured by X2 than in schedule T2 on the identical data item.Suppose, for instance, Transaction X1 formerly writes a data item Y in schedule T1, then in T2, the latest write procedure on Y must be accomplished by the transaction X1. Final Write: In the both the schedules, final write processes on every data item should satisfy.For instance, we can view that data item Y can be delivered numerous times in a schedule, but then the initial read operation on Y is known to be an initial read. Therefore, the initial read denotes the preliminary read procedure on a data item. Read vs Initial Read: Anyone can have confusion with the word-initial read.For illustration, if transaction X1 states a data item Y before transaction X2 in schedule T1, then in the specified schedule T2, X1 must-read Y before X2. Initial Read: In both the schedules, the initial read status of every data item should match in transactions.Suppose we have two schedules X1 and X2, that are known to remain view equivalent only if they match all the succeeding conditions: Let us see how to test whether the two DBMS schedules available are defined to remain view equivalent or not: Hadoop, Data Science, Statistics & others


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
